How to Setup a Static IP with PythonAnywhere and MySQL
Table of contents
Unfortunately, Python’s MSSQL implementations are extrapolations of C libraries and there is no clean way to insert a proxy directly into the implementation.
But never fear, we can use the QGTunnel solution to get around this limitation.
The setup is very similar to setting up QuotaGuard with MySQL, just with different ports involved.
We’re going to use the SOCKS proxy using the QGTunnel software.
To get started:
1) Download QGTunnel
Download and extract the qgtunnel package in the root directory of your app:
$ curl https://s3.amazonaws.com/quotaguard/qgtunnel-latest.tar.gz | tar xz
2) Setup the Tunnel
If you are using the Heroku CLI, you can log into our dashboard with the following command:
heroku addons:open quotaguardstatic
Or, if you prefer, you can login to our Admin Dashboard and go the Tunnels page to setup the tunnel.
Click Create a Tunnel. You should reach this screen below.
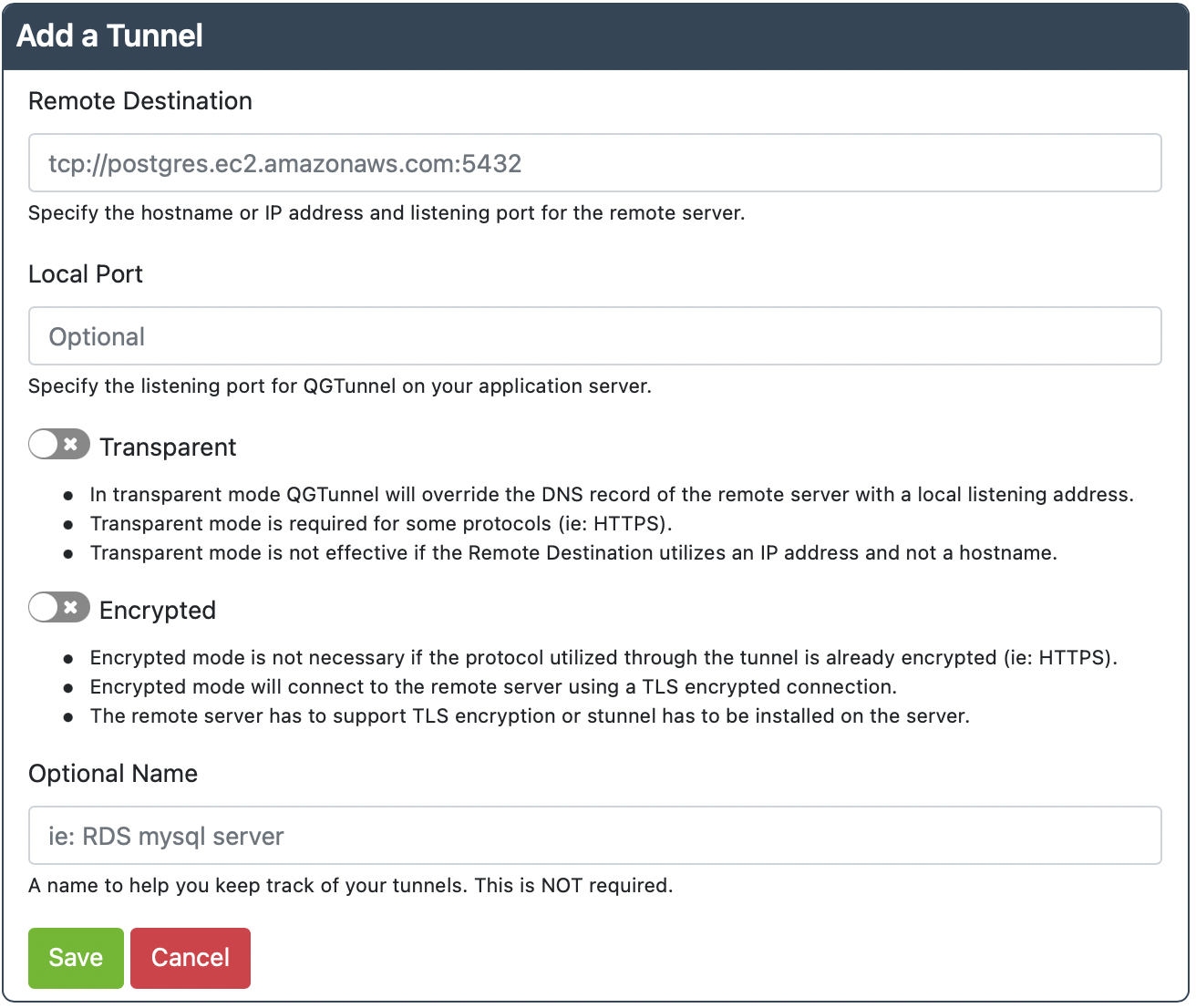
Remote Destination: tcp://hostname.for.your.server.com:1433
Local Port: 1433
Transparent: true
Encrypted: false
This setup assumes that the remote MYSQL: server is located at “hostname.for.your.server.com” and is listening on port 1433 (This is usually the default port.).
The Local Port is the port number that QGTunnel will listen on. In this example, we set it to 1433, but if you have another process using 1433, you may have to change it (ie: 1434).
Transparent Mode allows QuotaGuard to override the DNS for hostname.for.your.server.com to 127.0.0.1, which redirects traffic to the QGTunnel software. This means you can connect to either hostname.for.your.server.com or 127.0.0.1 to connect through the QGTunnel.
More information is available on transparent mode as you follow along in these instructions.
Encrypted Mode can be used to encrypt data end-to-end, but if your protocol is already encrypted then you don’t need to spend time setting it up. We believe MSSQL is already encrypted, but you should always double check.
Creating the tunnels in the dashboard is for convenience. Please see the last step (Harden Your Setup) for how to remove this dependency from your system.
3) Change Your Code to Connect Through the Tunnel (maybe)
You may have to change your code to connect through QGTunnel.
With transparent mode and matching Local and Remote ports you should not need to change your code. You can also connect to 127.0.0.1:1433.
Without transparent mode, you will want to connect to 127.0.0.1:1433.
4) Change your Procfile
Heroku Users: You have a procfile even if it’s not explicitly in your code base. To find it, log into the Heroku dashboard, click on the Resources tab, and you will see a list of your dyno processes. The text you see (like web npm start) next to each one acts as your Procfile if you do not have one explicitly in your code base.
Modify your app Procfile to prepend the QGTunnel application to your standard commands:
Before:
web: your-application your arguments
After:
web: bin/qgtunnel your-application your arguments
5) Setup the Environment Variable QUOTAGUARDSTATIC_URL to be Equal to your Connection URL in the Setup Page of our Dashboard
If you added us from a cloud provider (Azure, Cloudfoundry, Heroku, AWS, IBM Cloud, Pivotal, etc.) then this is usually done for you.
Please note that QGTunnel handles converting the HTTP URL and port to the SOCKS5 URL and port. So either of the connection URLs is fine.
6) Deploy
Commit and deploy your changes. Be sure to add bin/qgtunnel.
If you are using transparent mode, be sure vendor/nss_wrapper/libnss_wrapper.so is also committed.
7) (Optional) If problems arise…
By default all fatal errors encountered by the qgtunnel will be logged to your logs.
If this information is not enough you can enable verbose output mode by setting QGTUNNEL_DEBUG environment variable to true and restart the application while watching the logs.
Send any information in the logs (please redact any credentials, including your QuotaGuard connection URL) to our Support so we can help figure out the problem with you.
8) IMPORTANT: Harden Your Setup
This step is highly recommended as we do not have any SLA on our website, which can be out due to maintenance at any time.
By default qgtunnel will try to fetch configuration from the QuotaGuard API, but it also supports local configuration.
You can download a configuration file from the Dashboard by pressing Download Configuration on the Tunnels page.
Place the downloaded file into the root directory of your project under the .qgtunnel filename, commit and deploy.
With this file your application will not depend on the availability of our website during application startup.
Getting Help
The SOCKS wrapper is not straight forward to set up, or debug, so if you have any issues just get in contact with our Support and we’ll help you out.